Describe the Haploid and Diploid Life Cycles
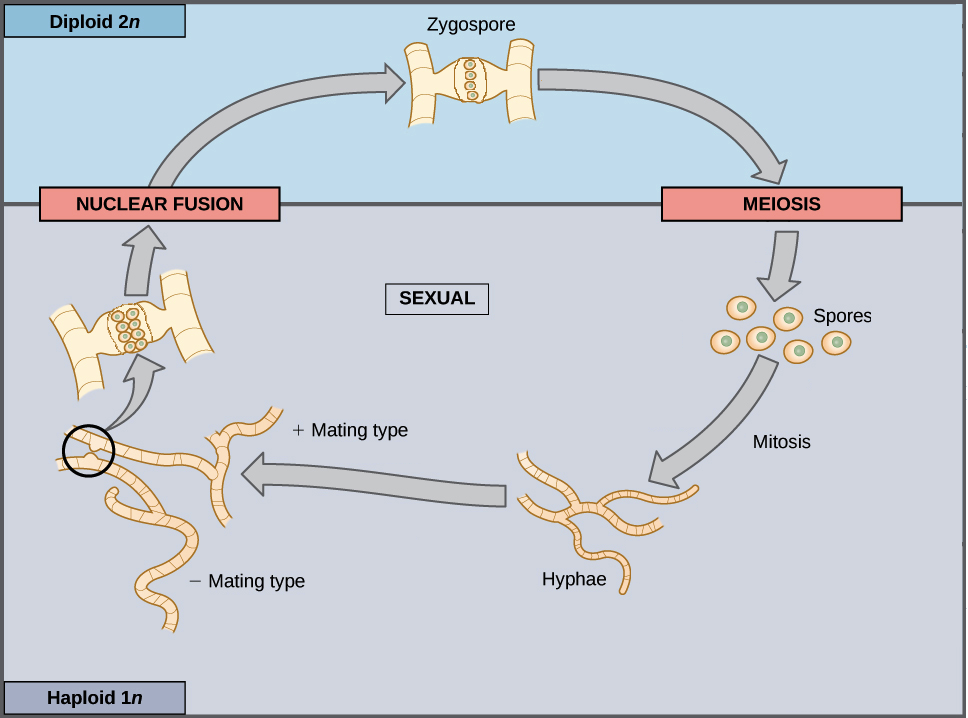
Expert Answer Zygomycetes has two phases in life cycle- i Asexual Reproduction and ii Sexual Reproduction. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells.

Plant Life Cycles Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
You MUST use the following vocabulary words CORRECTLY for credit.
. Mathematical models indicate that niche differences between ploidy phases may be a necessary condition for the evolution and maintenance of these life cycles. Fungi and some algae have this type of life cycle. What structures are haploid.
Determining the influence of mating system on the evolution of life cycles. Haplontic life cycle the haploid stage is multicellular and the diploid stage is a single cell meiosis is zygotic. Meiosis produces 4 gametes 1n ie.
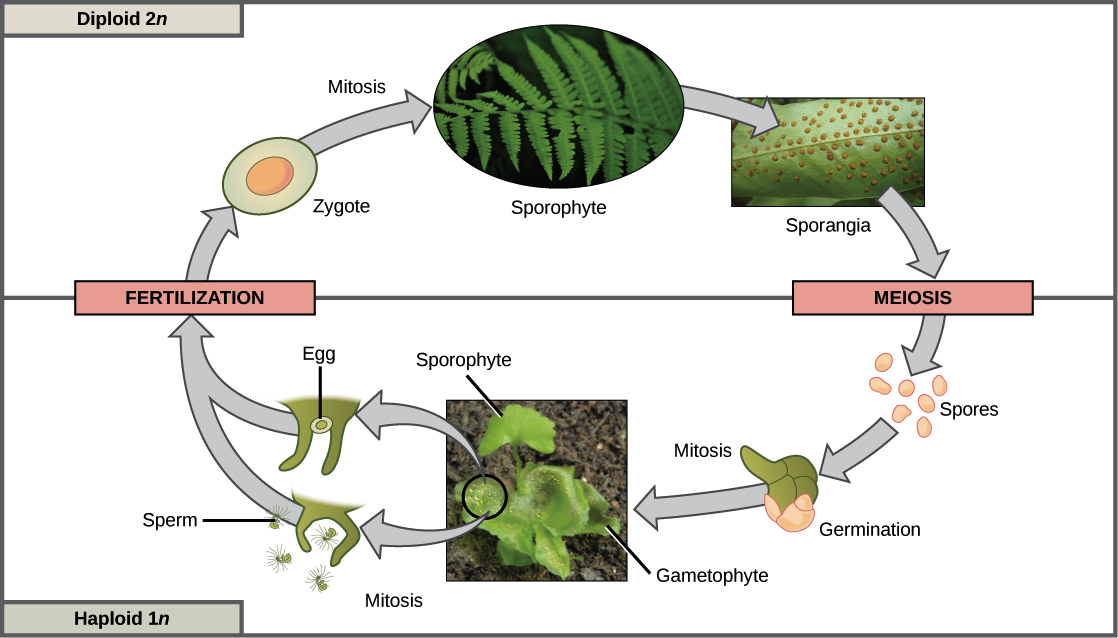
The sexual reproduction of the moss bryophyte life cycle alternates between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte phases. Although the evolutionary advantages of sexual reproduction have been extensively discussed much less attention has been paid to haploid and diploid phases of the sexual life cycle. As shown in the diagram below using a gamete-producing plant is named for its production by.
In haplodiplontic life cycles gametes are not the direct result of a meiotic division. Examples of diploid cells include blood cells skin cells and. The evolutionary stability of haploid-diploid life cycles is still controversial.
In a haploid-dominant life cycle the multicellular or sometimes unicellular haploid stage is the most obvious life stage and is often multicellular. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. In the diplontic life cycle the diploid stage or sporophyte is the dominant and independent stage of the plant and performs photosynthesis.
In the higher organism such as humans haploid cells are only used for sex cells. These mature gametes then fuse syngamy and developes into zygote 2n. Adult individuals are diploid each individual inheriting.
Sexual eukaryotic organisms are characterized by an alternation between haploid and diploid phases. The life cycle of fungi includes both haploid and diploid parts. Draw or describe how fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota reproduce beginning with a haploid spore landing in a nice spot and dividing through mitosis.
In regard to changes of ploidy there are 3 types of cycles. Examples of haploid cells are gametes male or female germ cells. During the asexual phase of reproduction a haploid mycelium grows and produces aerial hyphae via mitosis.
When egg and sperm merge they form a diploid zygote which grows into a diploid sporophyte. It is also the most common life cycle among plants since all land plants the vascular plants and the bryophytes are haploid-diploid. The _____-_____ life cycle is the simplest of the sexual life cycles haploid cells are the major of the life cycle - adults are haploids haploid cells under mitosis to produce gametes this type of life cycle is found in many protists fungi and some algae.
In many other eukaryotes however growth and development occur in both phases with substantial variability among. Describe the life cycle of a zygomycotic fungus such as Rhizopus. In a genetic sense the sporophyte is an intimate union of the gametophytes that produced.
Isogamy anisogamy and oogamy which through mitosis develops into mature gametes. Contrary to the haploid life histories sporophyte is present in a diploid life history and the gametophyte is absent. The multicellular haploid gametophyte and sporophytes.
Haploid cells are formed by the process of meiosis. This type of life cycle exhibits alternation of generations. Their chromosome number and function are different.
Here mitosis usually occurs at the diploid stage ie. The relative advantage of diploid versus haploid life cycles depends on the exact balance reached between masking and eliminating mutations. In vascular plants and animals somatic growth and develop- ment occur primarily in the diploid phase with the haploid phase reduced to the gametic cells.
This occurs when a multicellular 2n sporophyte SPT phase alternates with a. The land plant life cycle is known as a sporic for sporic meiosis dibiontic or haplodiplontic life cycle. The haploid phase is represented by single-cell gametes or few celled gametophytes.
In other words to complete a full circuit of its life cycle a land plant must produce two different types of multicellular organisms. In the higher organism such as humans all other cells beside sex cells are diploid. An alternation of generations defines the haploid-diploid or 1n-2n life cycle.
In this type of life cycle the single-celled zygote is the only diploid cell. Alternation of generations is when a diploid plant called a sporophyte gives rise to a haploid plant called a gametophyte then. Diploid sporophyte cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores The plant life cycle alternates between haploid and.
In a nutshell haploid gametophytes produce haploid gametes which can be sperm or eggs. The plant life cycle alternates between haploid and diploid generations. THE DIPLOID LIFE CYCLE.
The haploid-diploid life cycle is the most complex life cycle and thus has lots of variation. Diplontic life cycle the diploid stage is multicellular and haploid gametes are formed meiosis is gametic. Zygote and gametes are produced by meiosis.
Haplontic life cycle refers to a life cycle in which the main form is haploid with a diploid zygote being formed only briefly while diplontic life cycle refers to a life cycle in which the main form except for the gametes is diploid. Diploid cells undergo mitosis. The diploid plant that develops from the zygote via the embryo produces haploid spores by meiosis and is known as a sporophyte spore-plant.
Plants undergo a life cycle termed alternation of generations. Indicate haploid diploid and heterokayotic stages. We first describe the mating systems that we model with special reference to green and red algae Chlorophyta and Rhodophyta.
The reproduction of the haploid gametophytic plant is followed by the sexual method whereas the. The life cycles of all plants alternate between two includes both multicellular haploid organisms and multicellular generations of distinct multicellular organisms. Nevertheless experimental support for this prediction rema.
Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the haploid phase which. The relative lengths of these phases differ greatly in various taxa including as extremes those with one or the other phase reduced to a single cell. Diplohaplontic Life Cycle The diplohaplontic life cycle has equally prominent haploid and diploid phases which are represented by two distinct.

Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy
No comments for "Describe the Haploid and Diploid Life Cycles"
Post a Comment